Our Products
- Distribution Transformers
- Power Transformer
- Auto Recloser Circuit Breaker
- MV Overhead Switch with Break under SF6
- Air-Insulated Modular Cell
- Fused Compact RMU Cubicle
- Withdrawable Cell
- Aluminum Alloy Conductor
- Medium Voltage Cable, Low Voltage Cable
- Aerial Twisted Cable
- Junction And End Boxes
- Angled And Straight Separable Connector
- Public Lighting
- Manually Operated Aerial Switch
- Generator
- Onduleur
- MV Mobile Transformer Station
- Prefabricated Metal Transformer Substation
- HTA Mobile Transformer Station
- MV/LV Transformer Substation
- Voltage Regulator
- Rectifier
- Low Voltage Panel
Medium Voltage Cable, Low Voltage Cable
An electric cable is a cable used for the transport or distribution of MV or LV electrical energy, whether in alternating current or direct current and whatever the electrical voltage.
The electrical wires are often grouped together in an electrical cable with standardized colors (depending on the function), in order to recognize the role of each.


Advantages :
1)- Constitute the only possible solution in dense agglomerations,
2)- Are subtracted from atmospheric overvoltages (lightning),
3)- Do not cause interference with telecommunications circuits,
4)- Produce no interference with radio and television reception,
5)- Only possible solution for crossing large rivers or inlets when the distance to be crossed exceeds 3 km.
Disadvantages:
1)- Are much more expensive than airlines. The difference is greater the higher the voltage;
2)- Fault identification is tricky and slow,
3)- Repairs are expensive and sometimes difficult,
4)- Their armor and sheaths must be protected against the effects of corrosion due to stray currents,
5)- Risk of being damaged in the event of ground movements,
6)- Their insulation is likely to be damaged by a rise in temperature of the conductors in the event of an overload.
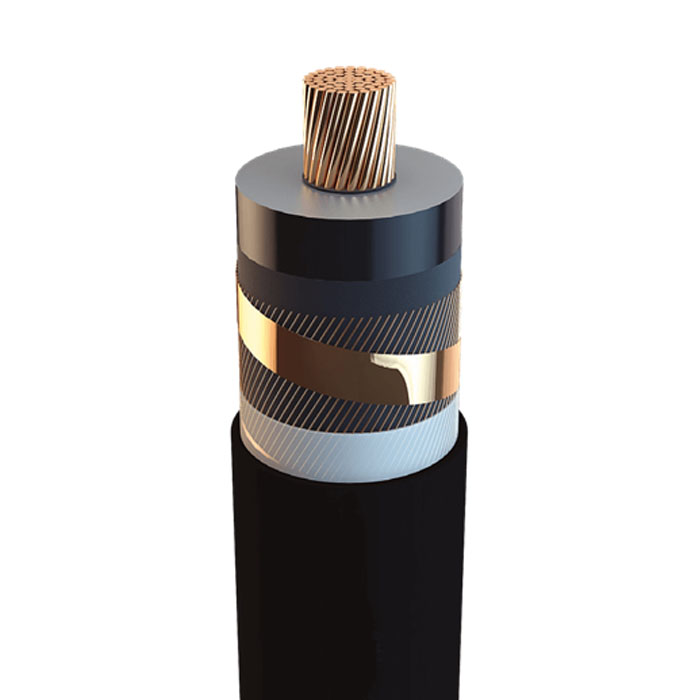


a) MV cable:

b) LV cable:

MV Underground Cable:
Depending on the nature of the Phases; we distinguish:
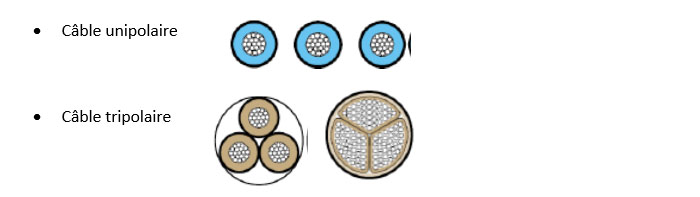
Depending on the type of insulation, we distinguish:
- Synthetic cable
- Impregnated paper insulated cable
• XLPE insulated cable
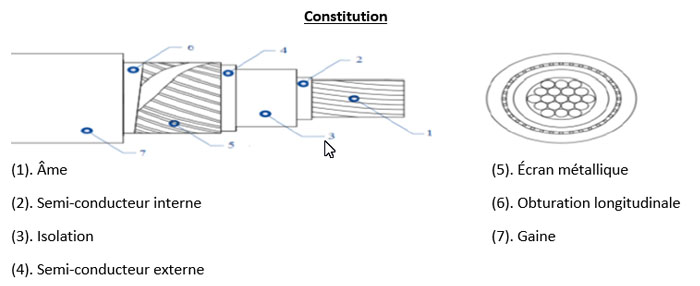
Core: Copper conductor,
Internal semiconductor: Screen applied to the conductor in thermostable semiconductor material,
Insulation: Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), in a tube in a dry atmosphere,
External semiconductor: Screen in thermostable and unknotable semiconductor material applied to the insulating envelope,
Metallic screen: Screen made of copper wires and tape,
Longitudinal shutter: Hygroscopic tape completely covering the screen
Sheath: Outer Halogen-free polyolefin.
-2) Three-pole cable
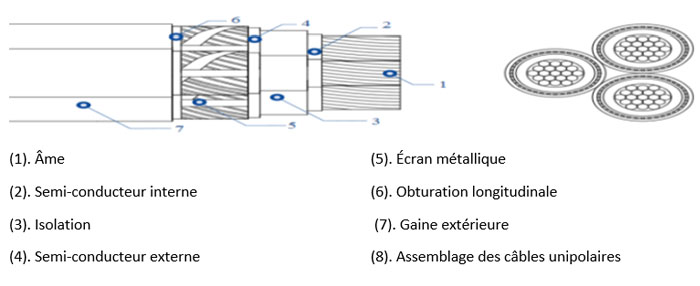

Role of Elements
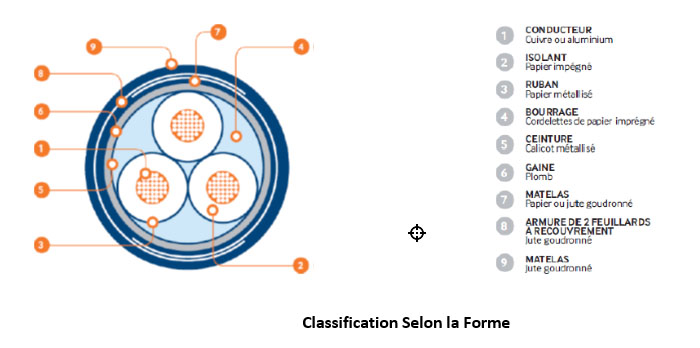
An electric cable always includes an active metal part (conductive core) whose role is to conduct the electric current, and one or more concentric layers of insulating and protective materials.
Conductive core: It can be massive, rigid or flexible or, even, extra flexible (welding cable). It is made of copper, aluminum or aluminum alloy.
Insulation: It is also called “envelope”. Its role is electric. The insulation material must have suitable electrical characteristics with the use of the cable. The insulations are extruded (PVC, PR, EPDM).
Stuffing: The purpose of stuffing is to fill the interstices between the conductors in order to give the cable a cylindrical shape.
Sheath: This is the simplest protection. It is extruded (Polychloroprene, halogen-free, for example). It can also jam and drain capacitive currents.
Armor: It is the protection against shocks. Armor can also act as a screen for the flow of short-circuit currents.
Shielding: Screens or shielding are not intended for mechanical protection but for electrical protection. Create a barrier to electrostatic fields outside the cables.
Others products

Low Voltage Panel

Rectifier (Battery Charger)

Voltage Regulator

